| S. No |
Photograph |
Photograph |
Technologies Crop varieties |
Descriptions |
Expected benefit |
Impact |
| 1. |
 |
 |
Agonda Goa |
Early maturing pig species supplementing pork supply in the market of hot humid climate of coast, registered as a third pig breed of the country (Id. INDIA_PIG_3500- AGONDAGOAN_09003 |
|
|
| 2. |
 |
 |
Goya Pig |
An improved breed of pig with 75% exotic large White Yorkshire and 25% local Agonda Goan species had better performance and adoptability in the hot humid climate of the coastal region |
|
|
| 3. |
 |
 |
Shweta Kapila |
Indigenous cattle registered in 2020, characterized as short to medium stature, white colored having strong adaptability in hot and humid coastal climate and resistant to diseases. Daily milk yield - 1.8 to 3.4 kg with (mean 2.8 kg) |
|
|
| 4. |
 |
 |
Boar semen extender |
Novel Boar Semen Extender (NBSE) which could preserve pig semen at 15-17 °C for a minimum period of 3 days. Patent granted on 1st January, 2021 (Patent No: 355114). |
|
|
| 5. |
 |
 |
Ornamental fish feed |
A cost-effective fish feed formulation a sinking type pellet (10 minutes for complete sinking, water stability 30-45 minutes) suitable for rearing ornamental fishes. It is used to obtain better growth, and colour in fishes. |
|
|
| 6. |
 |
 |
Feed block Technology using locally available livestock feed resources |
Standardized a process of making plain and compound livestock feed blocks using locally available feed resources like wild dry grass (Karad) and paddy straw. |
Besides, effective utilization of feed resources, this technology offers other benefits like cheaper storage, easy transportation, easy handling and reduced cost |
The technology helps to reduce the use of concentrate as well as maintain the milk yield in cattle yielding around 10 litre milk |
| 7. |
 |
 |
Standardized technology of artificial insemination in pigs, poultry and goats |
It is a reproductive technology for rapid genetic improvement of farm animals involving collection of semen from healthy male animal, processing and depositing them into the reproductive tract of a receptive female animal artificially using insemination gun or catheter |
|
Currently AI technology in pigs has been performed in and around 40 villages. 734 farmers were benefitted Generating employment of ≈1.37 lakh man-days translating to an income generation to the tune of Rs 9.6 crores |
| 8. |
 |
 |
Crossbred pig production technology |
Technology includes crossbred pig produced by mating Agonda Goan female and Large White Yorkshire male for producing the crossbred pig. |
|
Average birth weight (820.34±38.16g) Weaning weight at 40 days’ age 5.4 kg Weight at 10 months’ age 85 to 90kg Age of puberty 190days, Age of sexual maturity 220days,Age of first farrowing (335days) and better pork with (3.36cm) back fat thickness |
| 9. |
 |
 |
Artificial fish habitats for fish farmers |
The artificial fish habitats (AFH) - to provide refuges and breeding sites. Using underwater visual census (UVC) in Zuary estuary, 50 species were counted and species diversity were higher at deeper AFHs. Oysters, sponges and ascidia was highest on the deeper AFHs |
|
Institute technology supported conservation and aquatic diversity, besides increasing fish catch and net incomes of the fish farmers |
| 10. |
|
|
Standardization of diagnostics for detection of rotavirus |
RT-PCR test was standardized for the detection of the VP4 and VP7 genes of rotavirus. RNAPAGE, AGE methods were standardized for rapid detection of dsRNA of rotavirus from fecal samples |
|
|
| 11. |
 |
 |
Low-cost multispecies culture system for coastal region |
The culture system is designed to improve fish and mussel production in the coastal region using cage systems. The size of the cage: 2 m x 1.5 m x 2 m, Culture period: 8-10 months. Species cultured: Multi-species (red snapper, pearl spot, and green mussel). Mussel seeds collected from the wild were stocked in cotton mosquito net bags. |
|
The net profit and BC ratio of the system was Rs. 34000 and 2.4, respectively |
| 12. |
 |
 |
Technology for long term preservation of boar semen |
Protocol for long term preservation of boar semen using controlled-rate semen freezing, cryopreservation technology. Method involves controlled rate freezing of pig semen extended using indigenous semen diluent |
Successfully evaluated for in-vivo fertility status in female pigs using deep intra-uterine insemination procedure and viable piglets were born from frozen semen AI |
Overall conception rate increased by 47.37% and farrowing rate by 15.79%. |
| 13. |
 |
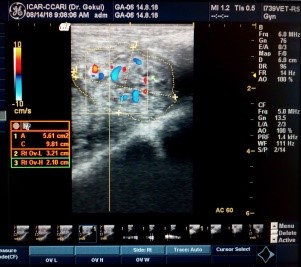 |
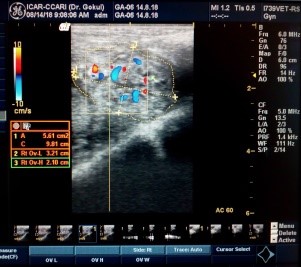
Digital colour doppler ultrasound imaging technology in reproductive management of livestock |
Standardized, Trans-abdominal and trans-rectal methods for scanning and imaging reproductive organs for diagnosing pregnancies, reproductive problems, monitor and assess the blood flow through internal organs using digital Color Doppler ultrasound imaging technique |
Very useful in assessing ovarian perfusion and functional status of reproductive system |
|
| 14. |
 |
 |
ICAR-CCARI Fish database |
Provides information on status, catch, species (a total of 300 species with systematic, description, size, food and feeding, utilization and gears used for fishing) and technology options for improving fish production in coastal ecosystems |
The database acts as a decision support system to the coastal fishermen. |
The total number of views/visitors to the data base are ≈10000/annum Link: https://kvknorthgoa.icar.gov.in/fishdb/ |
| 15. |
 |
 |
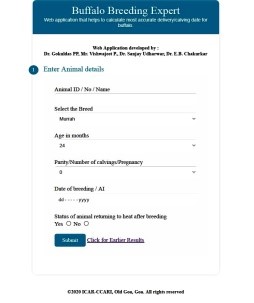
Web application- Buffalo breeding Expert |
Developed for buffalo breeding, herd management, reliable calving date and ideal weaning date for various breeds of buffaloes. It includes an expert system on scientific buffalo farming, management practices and indigenous buffalo breeds suitable for coastal climate. |
|
The total number of views/visitors to the webportal are 1500. Link:https://kvknorthgoa.icar.gov.in/buffalo/form.php |

